This page covers the stem group of the clade that contains the heterosporous lycophytes: the Orders Isoetales and Selaginellales.
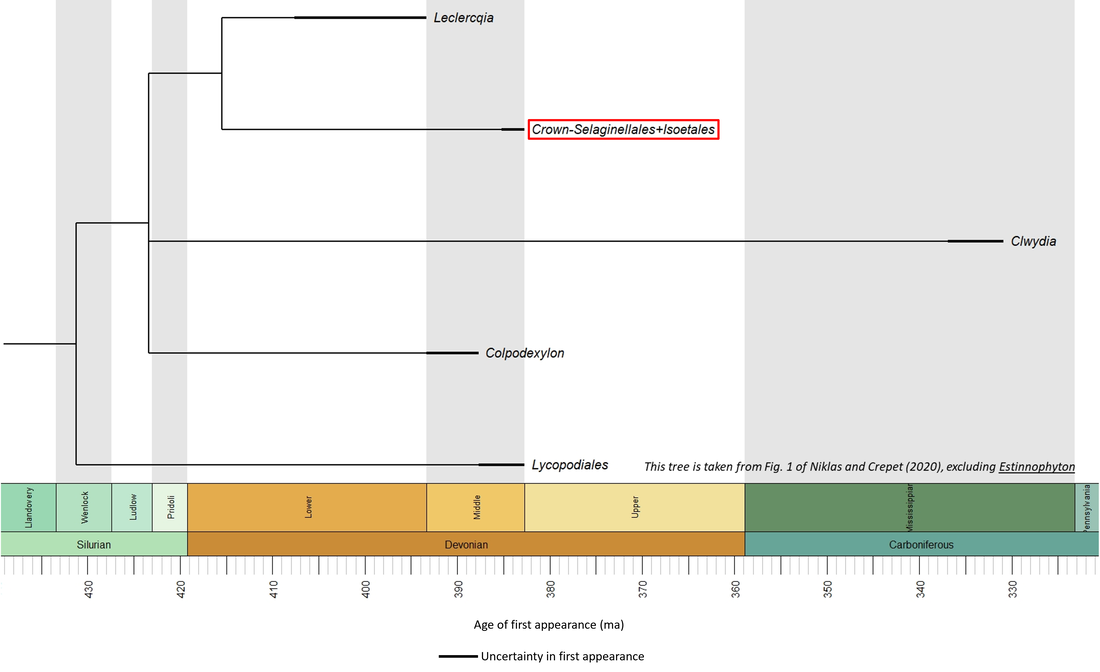
The fossils that comprise the stem group of the Isoetales/Selaginellales all belong to the extinct order Protolepidodendrales. Many descriptions of these fossils have been published, but hardly any phylogenetic trees have been published. One of the most recent forms the basis of the time tree shown below:
The fossils that comprise the stem group of the Isoetales/Selaginellales all belong to the extinct order Protolepidodendrales. Many descriptions of these fossils have been published, but hardly any phylogenetic trees have been published. One of the most recent forms the basis of the time tree shown below:
Figure 1. Time tree of the stem-(Isoetales/Selaginellales)
Note that the genus Estinnophyton has been excluded because of a divergent, and persistent, opinion that it belongs to the Euphyllophyta (e.g. Hao and Xue, 2013).
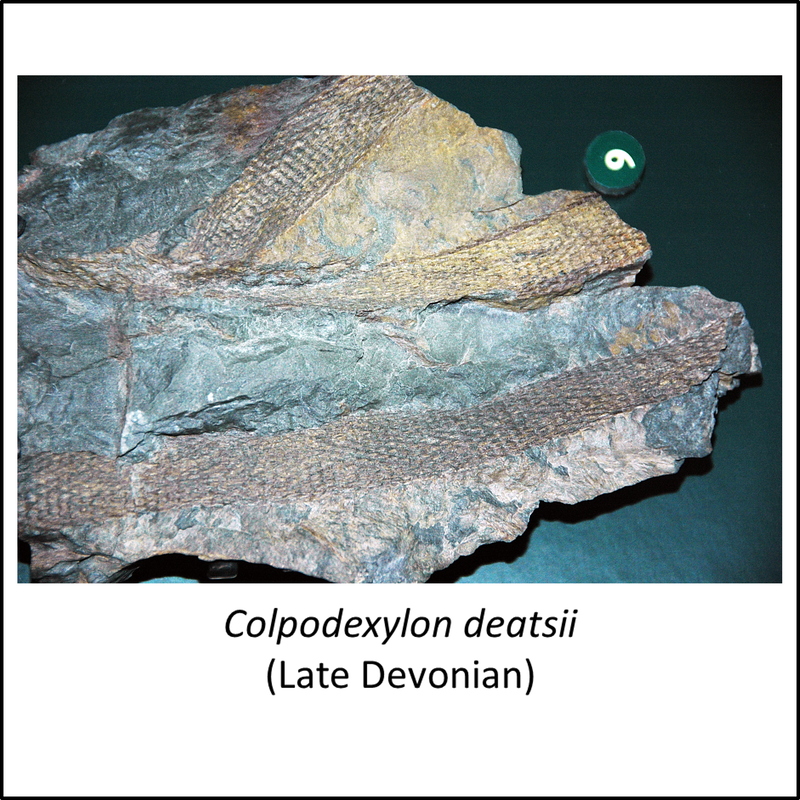
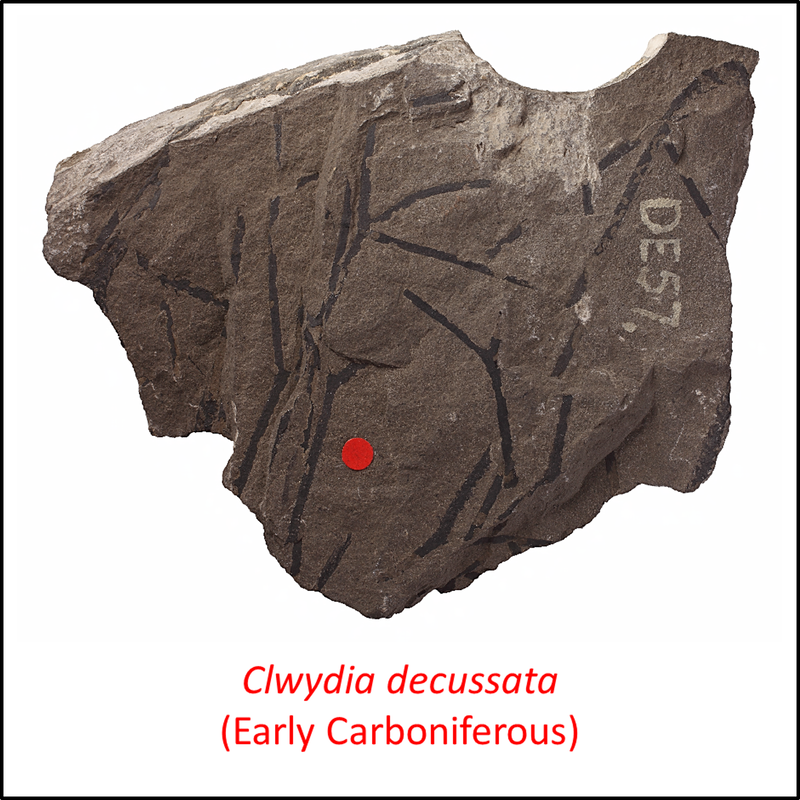
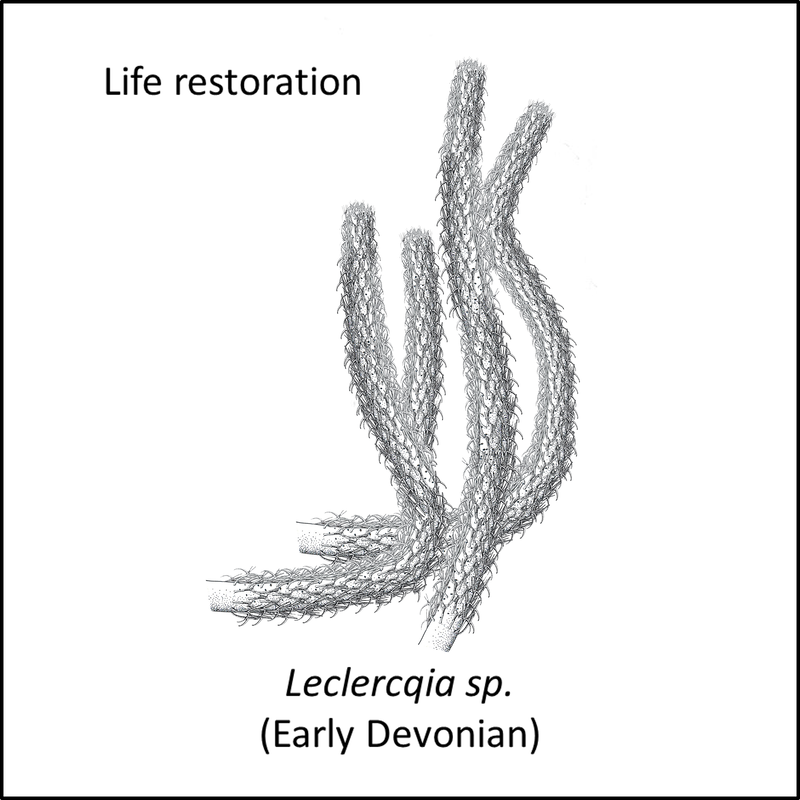
The oldest known member of the stem group of the Isoetales/Selaginellales clade is Leclercqia complexa, described from the Early Devonian (Emsian) Campbellton Formation at two localities on the Restigouche River in New Brunswick, Canada (Gensel and Albright, 2006; Niklas and Crepet, 2020). A comparable species of this genus, together with other members of the stem group for which images are available in the public domain, are shown below (to see a larger view, click on image):
The oldest known member of the stem group of the Isoetales/Selaginellales clade is Leclercqia complexa, described from the Early Devonian (Emsian) Campbellton Formation at two localities on the Restigouche River in New Brunswick, Canada (Gensel and Albright, 2006; Niklas and Crepet, 2020). A comparable species of this genus, together with other members of the stem group for which images are available in the public domain, are shown below (to see a larger view, click on image):
Names in red indicate that the fossil is younger than the oldest known crown-group fossil.
Figure 2. Images of stem-(Isoetales/Selaginellales)
The small number of images available prevents any assessment of evolutionary trends through the stem group.
Some idea of the nature of the transition from the stem group to the crown group of the Isoetales/Selaginellales can be derived from a comparison of the above images with the examples of crown-Isoetales/Selaginellales shown below:
Some idea of the nature of the transition from the stem group to the crown group of the Isoetales/Selaginellales can be derived from a comparison of the above images with the examples of crown-Isoetales/Selaginellales shown below:
Figure 3. Examples of crown-Isoetales/Selaginellales
The above time tree (Figure 1) indicates that the Isoetales/Selaginellales stem group developed from Early to Middle Devonian time, representing a stem-to-crown transition of at least 8.1 million years.
References
Bateman, R. M., & DiMichele, W. A. (1994). Heterospory: the most iterative key innovation in the evolutionary history of the plant kingdom. Biological Reviews, 69(3), 345-417.
Field, A. R., Testo, W., Bostock, P. D., Holtum, J. A., & Waycott, M. (2016). Molecular phylogenetics and the morphology of the Lycopodiaceae subfamily Huperzioideae supports three genera: Huperzia, Phlegmariurus and Phylloglossum. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 94, 635-657.
Gensel, P. G., & Albright, V. M. (2006). Leclercqia complexa from the Early Devonian (Emsian) of northern New Brunswick, Canada. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 142(3-4), 103-121.
Hao, S., & Xue, J. (2013). Earliest record of megaphylls and leafy structures, and their initial diversification. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58, 2784-2793.
Niklas, K. J., & Crepet, W. L. (2020). Morphological (and not anatomical or reproductive) features define early vascular plant phylogenetic relationships. American Journal of Botany, 107(3), 477-488.
Schneider, H., & Pryer, K. M. (2002). Structure and function of spores in the aquatic heterosporous fern family Marsileaceae. International Journal of Plant Sciences, 163(4), 485-505.
Field, A. R., Testo, W., Bostock, P. D., Holtum, J. A., & Waycott, M. (2016). Molecular phylogenetics and the morphology of the Lycopodiaceae subfamily Huperzioideae supports three genera: Huperzia, Phlegmariurus and Phylloglossum. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 94, 635-657.
Gensel, P. G., & Albright, V. M. (2006). Leclercqia complexa from the Early Devonian (Emsian) of northern New Brunswick, Canada. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 142(3-4), 103-121.
Hao, S., & Xue, J. (2013). Earliest record of megaphylls and leafy structures, and their initial diversification. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58, 2784-2793.
Niklas, K. J., & Crepet, W. L. (2020). Morphological (and not anatomical or reproductive) features define early vascular plant phylogenetic relationships. American Journal of Botany, 107(3), 477-488.
Schneider, H., & Pryer, K. M. (2002). Structure and function of spores in the aquatic heterosporous fern family Marsileaceae. International Journal of Plant Sciences, 163(4), 485-505.
Image credits – Stem-Isoetales/Selaginellales
- Figure 2 (Colpodexylon deatsii): James St. John, CC BY 2.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
- Figure 2 (Clwydia decussata): British Geologica; Survey, under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
- Figure 2 (Leclercqia cf. complexa, fossil): Open Access article Capel, E., Cleal, C. J., Xue, J., Monnet, C., Servais, T., & Cascales-Miñana, B. (2022). The Silurian–Devonian terrestrial revolution: diversity patterns and sampling bias of the vascular plant macrofossil record. Earth-Science Reviews, 231, 104085.
- Figure 2 (Leclercqia sp., life restoration): Falconaumanni, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
- Figure 3 (Lepidophloios sp.): Falconaumanni, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
- Figure 3 (Lepidodendron sp.): Open Access article Wang, Q., Xu, H., & Shen, S. (2013). Notes on the Key Taxonomic Characters of Arborescent Lycopsid Stem Adpressions.