The seed plants (Subphylum Spermatophytina, Phylum Tracheophyta) comprise seed-bearing vascular plants, of which more than 300,000 species of extant seed-bearing vascular plants are known (Encyclopaedia Britannica). They represent a clade which is known as the Spermatophyta and consists of the gymnosperms and the angiosperms.
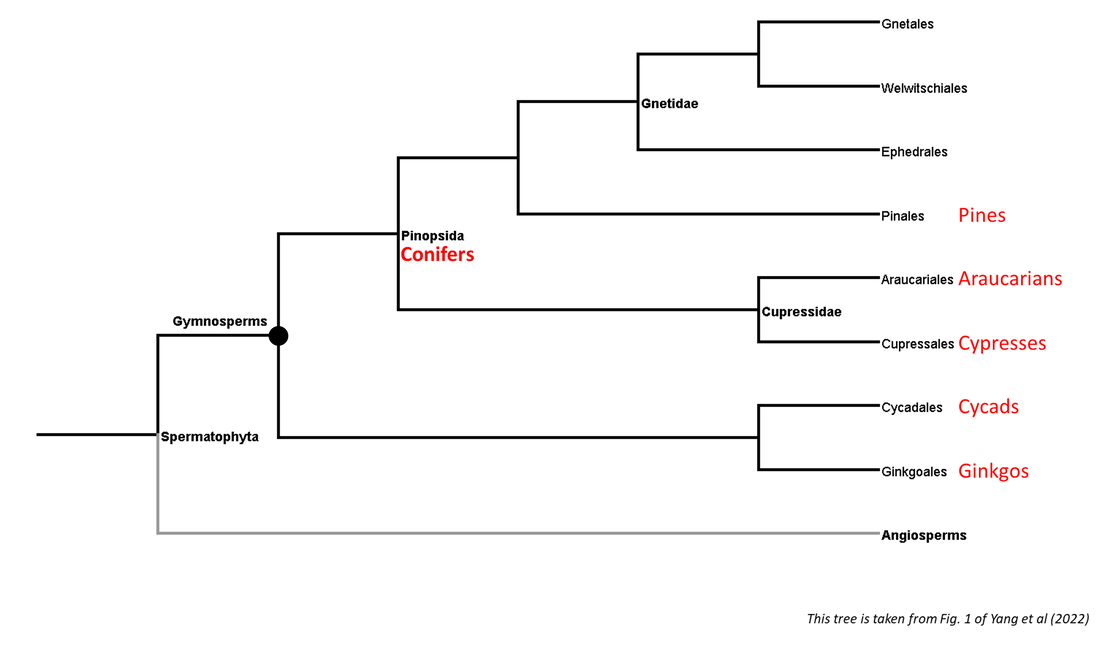
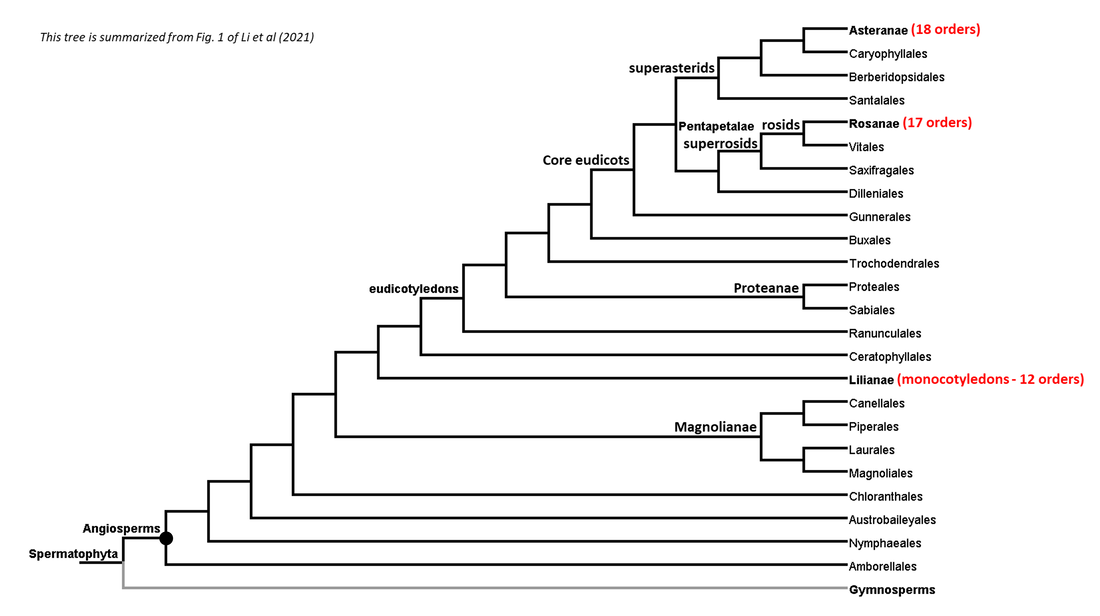
Summaries of the phylogenies of the gymnosperm and angiosperm clades are shown below:
Summaries of the phylogenies of the gymnosperm and angiosperm clades are shown below:
Figure 1. Summarized phylogenetic tree of the gymnosperms
Figure 2. Summarized phylogenetic tree of the angiosperms
The angiosperms will not be considered further, for two reasons:
Each page of this website deals with a single branch of the phylogenetic tree. Links to the pages corresponding to the branches shown above (those for which adequate data are available) can be found under the Navigation tab above.
The tetrapod stem branches not represented in this website are listed in the following table. In each case the column highlighted by the letter X indicates the reason for not including that branch:
- There is no consensus as to which fossils, if any, belong to the angiosperm stem line (Doyle, 2018; Bateman, 2020; Coiro et al, 2020; Benton et al, 2022). This problem is one manifestation of Darwin’s statement in 1879 that “The rapid development as far as we can judge of all the higher plants within recent geological times is an abominable mystery” (quoted in Friedman, 2009). Even though Darwin’s “abominable mystery” applied not to the origin of the angiosperms but to their rapid diversification during the Early Cretaceous (Friedman, 2009), the phrase has commonly been used to express the continuing difficulty of tracing the origin of the flowering plants in the fossil record (Bateman, 2020).
- The phylogeny of the angiosperm crown group is still unstable (Li et al, 2021; Guo et al, 2021). Furthermore, studies with fossil calibrations of molecular clock of clade ages (e.g. Magallón et al, 2015; Barba‐Montoya et al, 2018; Li et al, 2019) mention very few stem-group fossils that have been unequivocally defined for the constituent orders and higher clades within the angiosperms.
Each page of this website deals with a single branch of the phylogenetic tree. Links to the pages corresponding to the branches shown above (those for which adequate data are available) can be found under the Navigation tab above.
The tetrapod stem branches not represented in this website are listed in the following table. In each case the column highlighted by the letter X indicates the reason for not including that branch:
This page thus covers the stem-group seed plants.
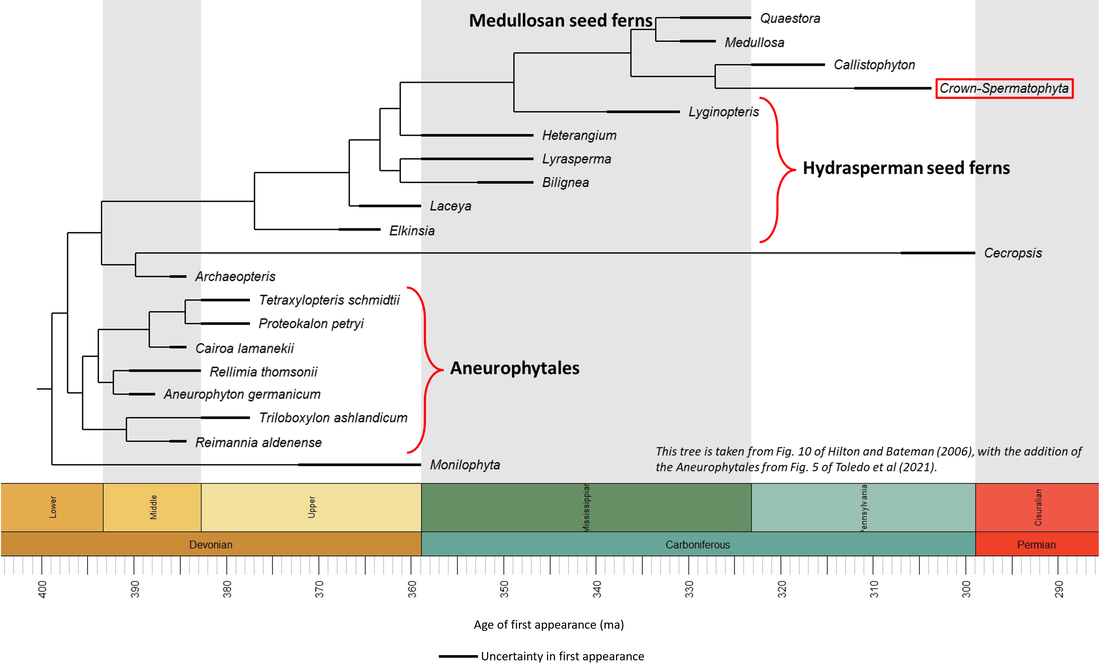
An interpretation of the phylogeny of the stem-Spermatophyta, based on two publications, is shown in the time tree below:
An interpretation of the phylogeny of the stem-Spermatophyta, based on two publications, is shown in the time tree below:
Figure 3. Time tree of the stem-Spermatophyta
The oldest known member of the seed plant stem group is Aneurophyton germanicum, described from Middle Devonian (Late Eifelian) sediments in the Massif de la Vesdre at Goé, Belgium (Momont et al, 2012; Toledo et al, 2021). This species is illustrated below, together with other stem group fossils for which images are available in the public domain (click on image for a larger view):
Figure 4. Images of stem-Spermatophyta
The above images are ordered from most basal to most crownward, and it seems possible to suggest tentatively that there is a trend from primitive-looking trees such as Aneurophyton through Tetraxylopteris to trees that look somewhat more like those of the present day (Archaeopteris).
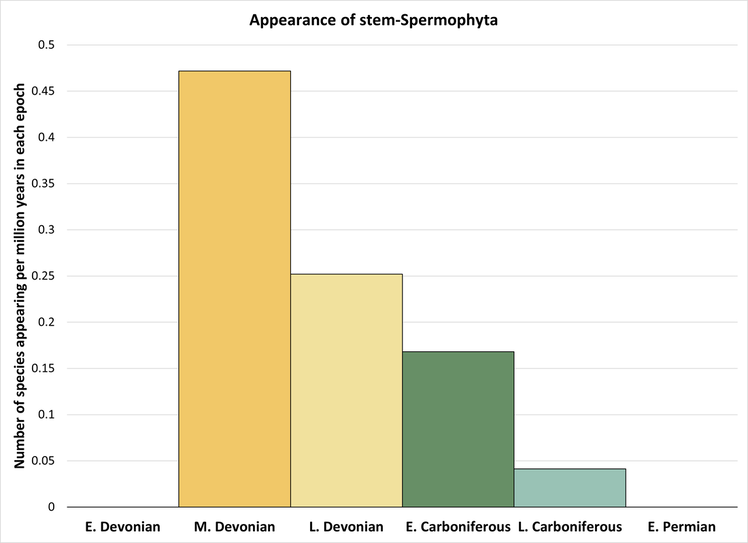
As indicated in Figure 1, the spermatophyte stem-to-crown transition took place over a period of at least 47 million years, from Middle Devonian to Late Carboniferous time. However, the highest rate of evolutionary change took place during the Middle Devonian, as indicated below:
As indicated in Figure 1, the spermatophyte stem-to-crown transition took place over a period of at least 47 million years, from Middle Devonian to Late Carboniferous time. However, the highest rate of evolutionary change took place during the Middle Devonian, as indicated below:
Figure 5. Rate of appearance of stem-group spermatophytes (predating the crown group and including only the species shown in Figure 1)
References
Barba‐Montoya, J., Dos Reis, M., Schneider, H., Donoghue, P. C., & Yang, Z. (2018). Constraining uncertainty in the timescale of angiosperm evolution and the veracity of a Cretaceous Terrestrial Revolution. New Phytologist, 218(2), 819-834.
Bateman, R. M. (2020). Hunting the Snark: the flawed search for mythical Jurassic angiosperms. Journal of Experimental Botany, 71(1), 22-35.
Benton, M. J., Wilf, P., & Sauquet, H. (2022). The Angiosperm Terrestrial Revolution and the origins of modern biodiversity. New Phytologist, 233(5), 2017-2035.
Bremer, K. (1985). Summary of green plant phylogeny and classification. Cladistics, 1(4), 369-385.
Coiro, M., Martínez, L. C., Upchurch, G. R., & Doyle, J. A. (2020). Evidence for an extinct lineage of angiosperms from the Early Cretaceous of Patagonia and implications for the early radiation of flowering plants. New Phytologist, 228(1), 344-360.
Doyle, J. A. (2018). Phylogenetic analyses and morphological innovations in land plants. Annual Plant Reviews online, 1-50.
Friedman, W. E. (2009). The meaning of Darwin's “abominable mystery”. American Journal of Botany, 96(1), 5-21.
Guo, X., Fang, D., Sahu, S. K., Yang, S., Guang, X., Folk, R., ... & Liu, H. (2021). Chloranthus genome provides insights into the early diversification of angiosperms. Nature communications, 12(1), 6930.
Li, H. T., Yi, T. S., Gao, L. M., Ma, P. F., Zhang, T., Yang, J. B., ... & Wang, H. (2019). Origin of angiosperms and the puzzle of the Jurassic gap. Nature Plants, 5(5), 461-470.
Li, H. T., Luo, Y., Gan, L., Ma, P. F., Gao, L. M., Yang, J. B., ... & Li, D. Z. (2021). Plastid phylogenomic insights into relationships of all flowering plant families. BMC biology, 19(1), 1-13.
Magallón, S., Gómez‐Acevedo, S., Sánchez‐Reyes, L. L., & Hernández‐Hernández, T. (2015). A metacalibrated time‐tree documents the early rise of flowering plant phylogenetic diversity. New Phytologist, 207(2), 437-453.
Momont, N., Gerrienne, P., & Prestianni, C. (2012). Aneurophyton germanicum (Aneurophytales-Progymnosperms) from the Middle Devonian of Belgium and Germany. Japanese Journal of Palynology, 58 (Special), 156-157.
Toledo, S., Bippus, A. C., Atkinson, B. A., Bronson, A. W., & Tomescu, A. M. (2021). Taxon sampling and alternative hypotheses of relationships in the euphyllophyte plexus that gave rise to seed plants: insights from an Early Devonian radiatopsid. New Phytologist, 232(2), 914-927.
Yang, Y., Ferguson, D. K., Liu, B., Mao, K. S., Gao, L. M., Zhang, S. Z., ... & Zhang, Z. X. (2022). Recent advances on phylogenomics of gymnosperms and a new classification. Plant Diversity, 44(4), 340-350.
Bateman, R. M. (2020). Hunting the Snark: the flawed search for mythical Jurassic angiosperms. Journal of Experimental Botany, 71(1), 22-35.
Benton, M. J., Wilf, P., & Sauquet, H. (2022). The Angiosperm Terrestrial Revolution and the origins of modern biodiversity. New Phytologist, 233(5), 2017-2035.
Bremer, K. (1985). Summary of green plant phylogeny and classification. Cladistics, 1(4), 369-385.
Coiro, M., Martínez, L. C., Upchurch, G. R., & Doyle, J. A. (2020). Evidence for an extinct lineage of angiosperms from the Early Cretaceous of Patagonia and implications for the early radiation of flowering plants. New Phytologist, 228(1), 344-360.
Doyle, J. A. (2018). Phylogenetic analyses and morphological innovations in land plants. Annual Plant Reviews online, 1-50.
Friedman, W. E. (2009). The meaning of Darwin's “abominable mystery”. American Journal of Botany, 96(1), 5-21.
Guo, X., Fang, D., Sahu, S. K., Yang, S., Guang, X., Folk, R., ... & Liu, H. (2021). Chloranthus genome provides insights into the early diversification of angiosperms. Nature communications, 12(1), 6930.
Li, H. T., Yi, T. S., Gao, L. M., Ma, P. F., Zhang, T., Yang, J. B., ... & Wang, H. (2019). Origin of angiosperms and the puzzle of the Jurassic gap. Nature Plants, 5(5), 461-470.
Li, H. T., Luo, Y., Gan, L., Ma, P. F., Gao, L. M., Yang, J. B., ... & Li, D. Z. (2021). Plastid phylogenomic insights into relationships of all flowering plant families. BMC biology, 19(1), 1-13.
Magallón, S., Gómez‐Acevedo, S., Sánchez‐Reyes, L. L., & Hernández‐Hernández, T. (2015). A metacalibrated time‐tree documents the early rise of flowering plant phylogenetic diversity. New Phytologist, 207(2), 437-453.
Momont, N., Gerrienne, P., & Prestianni, C. (2012). Aneurophyton germanicum (Aneurophytales-Progymnosperms) from the Middle Devonian of Belgium and Germany. Japanese Journal of Palynology, 58 (Special), 156-157.
Toledo, S., Bippus, A. C., Atkinson, B. A., Bronson, A. W., & Tomescu, A. M. (2021). Taxon sampling and alternative hypotheses of relationships in the euphyllophyte plexus that gave rise to seed plants: insights from an Early Devonian radiatopsid. New Phytologist, 232(2), 914-927.
Yang, Y., Ferguson, D. K., Liu, B., Mao, K. S., Gao, L. M., Zhang, S. Z., ... & Zhang, Z. X. (2022). Recent advances on phylogenomics of gymnosperms and a new classification. Plant Diversity, 44(4), 340-350.
Image credits – stem-Spermatophyta
- Figure 4 (Rellimia sp.): From Open Access article Harrison, C. J., & Morris, J. L. (2018). The origin and early evolution of vascular plant shoots and leaves. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 373(1739), 20160496.
- Figure 4 (Aneurophyton germanicum, fossil): Ghedoghedo, CC BY-SA 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
- Figure 4 (Aneurophyton germanicum, life restoration): Ghedoghedo, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
- Figure 4 (Tetraxylopteris sp., fossil): Skye McDavid, CC BY 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
- Figure 4 (Tetraxylopteris sp., life restoration): Falconaumanni, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
- Figure 4 (Archaeopteris macilenta, fossil): Photographed by Bob James (owner of website) at Denver Museum of Nature & Science, August 2023.
- Figure 4 (Archaeopteris macilenta, life restoration): Retallack, CC BY-SA 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
- Figure 4 (Elkinsia sp.): Zeiram1990 aka Georgi Ivanov on Fandom under CC BY-SA license
- Figure 4 (Heterangium americanum): Photo by John Hall, Botanical Society of America, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
- Figure 4 (Lyginopteris baeumleri): Daderot, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
- Figure 4 (Medullosa stellata): Ghedoghedo, CC BY-SA 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons